Manual¶
Quick Start¶
To run the examples, just download the data and start the python console. We can then import fANOVA and start it by typing
>>> from fanova import fANOVA
>>> import csv
>>> path = os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__))
>>> X = np.loadtxt(path + '/example_data/online_lda/online_lda_features.csv', delimiter=",")
>>> Y = np.loadtxt(path + '/example_data/online_lda/online_lda_responses.csv', delimiter=",")
>>> f = fANOVA(X,Y)
This creates a new fANOVA object and fits the Random Forest on the specified data set.
To compute now the marginal of the first parameter type:
>>> f.quantify_importance((0, ))
0.075414122571199116
fANOVA also allows to specify parameters by their names.
>>> f.quantify_importance(("Col0", ))
0.075414122571199116
Advanced¶
If you want the fANOVA only a certain quantiles (let’s say between 10% and 25%) of the data you can call it by:
>>> f = fANOVA(X,Y)
>>> f.set_cutoffs(quantile=(10, 25))
Furthermore fANOVA now supports cutoffs on the y values. These will exclude parts of the parameters space where the prediction is not within the provided cutoffs.
>>> f.set_cutoffs(cutoffs=(-np.inf, np.inf))
You can also specify the number of trees in the random forest as well as the minimum number of points to make a new split in a tree or your already specified configuration space by:
>>> f = fANOVA(X,Y, config_space=config_space, num_trees=30, min_samples_split=3)
More functions¶
- f.get_most_important_pairwise_marginals(n)
Returns the n most important pairwise marginals
- f.get_most_important_pairwise_marginals(params)
Returns the pairwise marginals of all elements in the list.
- f.get_triple_marginals(params)
Returns the marginals of all possible triplets in the list. They are sorted by importance.
- fANOVA.marginal_mean_variance_for_values(p, v)
Computes the mean and standard deviation of the parameter (or parameterlist) p for a certain value v
pysmac¶
In order to run fANOVA on pysmac output:
>>> import pysmac.utils.pysmac_fanova as pysmac_fanova
>>> fanova = pysmac_fanova.smac_to_fanova('path_to/pysmac_output_dir/out/scenario', 'path_to/merged_states')
Visualization¶
To visualize the single and pairwise marginals, we have to create a visualizer object first containing the fanova object, configspace and directory
>>> import fanova.visualizer
>>> vis = fanova.visualizer.Visualizer(f, config_space, "./plots/")
We can then plot single marginals by
>>> vis.plot_marginal(1)
what should look like this
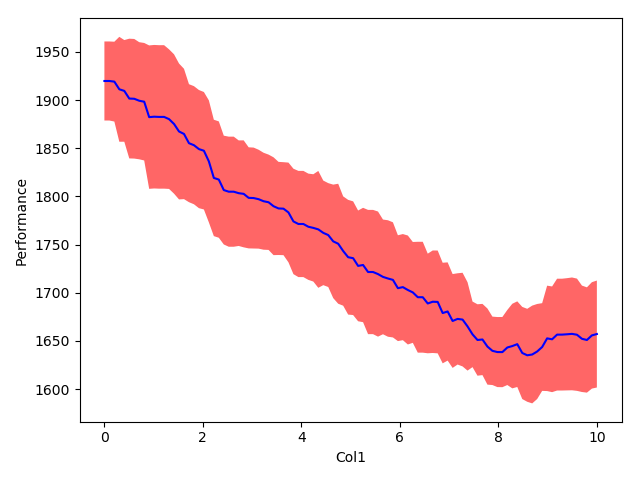
The same can been done for pairwise marginals
>>> vis.plot_pairwise_marginal([0,1])
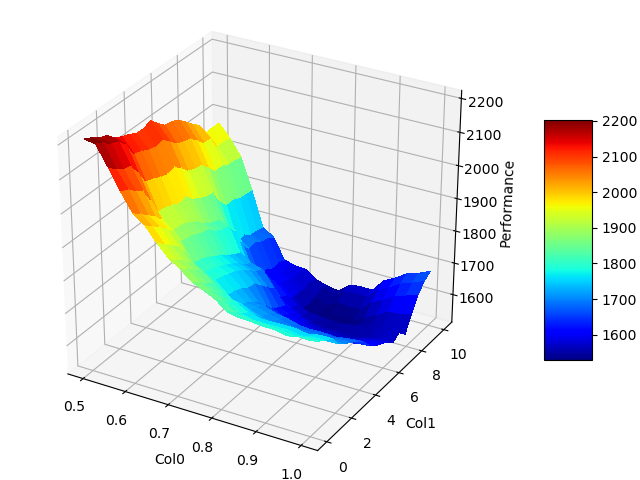
If you are just interested in the N most important pairwise marginals you can plot them through:
>>> create_most_important_pairwise_marginal_plots(dir, n)
and fANOVA will save those plot in dir. However, be aware that to create the plots fANOVA needs to compute all pairwise marginal, which can take awhile!
If you’re not interested in the plot itself, but want to extract the values for your own plots, simply call
>>> vis.generate_marginal(0)
At last, all plots can be created together and stored in a directory with
>>> vis.create_all_plots()
How to load interactive plots¶
You will also find an extra directory in your specified plot directory called ‘interactive_plots’ in which you can find all interactive pairwise plots as pickle files.
>>> import pickle
>>> figx = pickle.load(open('/interactive_plots/param1_param2.fig.pickle', 'rb'))
>>> figx.show()